Cylinder Swept Volume (Vc):
where:
Vc= cylinder swept volume [cm3
(cc) or L]
Ac = cylinder area [cm2
or cm2/100]
dc = cylinder diameter [cm or
cm/10]
L = stroke length (the distance between
the TDC and BDC) [cm or cm/10]
BDC = Bottom Dead Center
TDC = Top Dead Center
* Increase the diameter or the stroke length will increase
the cylinder volume, the ratio between the cylinder diameter/cylinder stroke
called “bore/stroke” ratio.
- “bore/stroke” >1 is called over square engine,
and is used in automotive engines
- “bore/stroke” =1 is called square engine
- “bore/stoke” <1 is called= under square engine,
and is used in tractor engine
Engine Swept Volume (Ve):
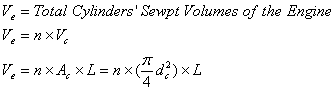
where:
Ve = engine swept volume [cm3
(cc) or L]
n = number of cylinders
Vc = cylinder swept volume [cm3
(cc) or L]
Ac =
cylinder area [cm2 or cm2/100]
dc = cylinder
diameter [cm or cm/10]
* The units of cylinder swept volume is measured in (cm3,
cubic centimeter (cc), or liter)
- Ve for small engines, 4 cylinder engines is (750
cc:1300 cc)
- Ve for big engine, 8 cylinder engines is (1600
cc:2500 cc)
Compression Ratio (r):
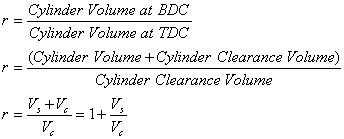
where:
r = compression ratio
Vs = cylinder swept volume
(combustion chamber volume) [cc, L, or m3]
Vc = cylinder volume [cc,
L, or m3]
* Increase the compression ratio increase engine power
- r (gasoline engine) = 7:12, the upper limit is engine pre
ignition
- r (diesel engine) = 10:18, the upper limit is the stresses
on engine parts
Engine Volumetric
Efficiency (hv):
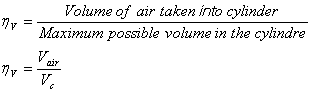
where:
hV
= volumetric efficiency
Vair = volume of air taken
into cylinder [cc, L, or m3]
Vc = cylinder swept volume
[cc, L, or m3]
* Increase the engine volumetric efficiency increase engine
power
- Engine of normal aspiration has a volumetric efficiency of
80% to 90%
- Engine volumetric efficiency can be increased by using:
(turbo and supper charger can increase the volumetric efficiency
by 50%)
Engine Indicated Torque (Ti):
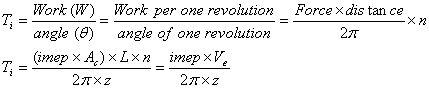
where:
Ti = engine indicated torque
[Nm]
imep = indicated mean effective pressure [N/m2]
Ac = cylinder area
[m2]
L = stroke length [m]
z = 1 (for 2 stroke engines), 2 (for 4
stroke engines)
n = number of cylinders
θ = crank shaft angle
[1/s]
Engine Indicated Power (Pi):
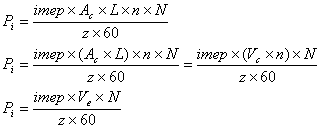 ,
,
where:
imep = is the indicated mean effective
pressure [N/m2]
Ac = cylinder area [m2]
L = stroke length [m]
n = number of cylinders
N = engine speed [rpm]
z = 1 (for 2 stroke engines), 2 (for 4
stroke engines)
Vc = cylinder swept volume [m3]
Ve = engine swept volume [m3]
Ti = engine indicated torque
[Nm]
ω = engine angular speed [1/s]
Engine Mechanical
Efficiency (hm):
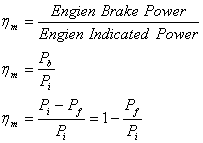
where:
hm
= mechanical efficiency
Pb = engine brake power [kW]
Pi = engine indicated power
[kW]
Pf = engine friction power
[kW]
Engine Specific Fuel
Consumption (SFC):
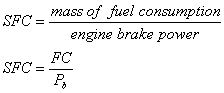
where:
SFC = specific fuel consumption
[(kg/h)/kW, kg/(3600 s x kW), kg/(3600 kJ)]
FC = fuel consumption [kg/h]
Pb = brake power [kW]
Engine Thermal Efficiency
(hth):
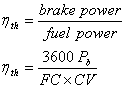
where:
hth
= thermal efficiency
Pb = brake power [kW]
FC = fuel consumption [kg/h = (fuel
consumption in L/h) x (ρ in kg/L)]
CV = calorific value of kilogram fuel
[kJ/kg]
ρ = relative density of fuel [kg/L]
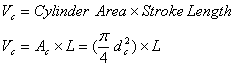
No comments:
Post a Comment